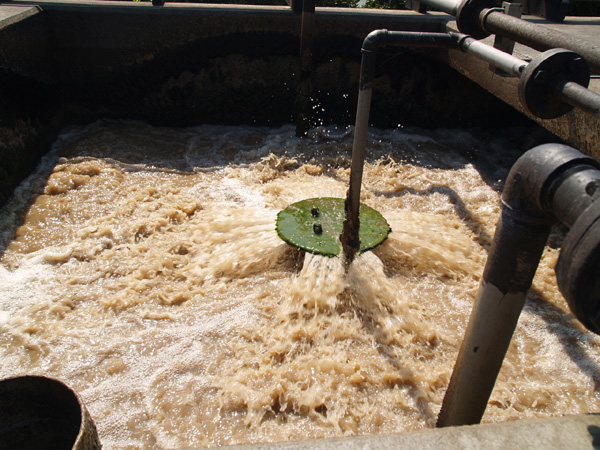

Sludge treatment is extremely important from the perspective of environmental protection and compliance with legal regulations. In this article, we will explain what sludge is, its characteristics and sources, and introduce the commonly used methods and technologies for sludge treatment.
※This description is based on Japanese legal regulations. Please note that regulations may vary by country.
Contents
What is Sludge?
Sludge refers to the solids or semi-solids generated during the wastewater treatment process. The main types are as follows:
- Sewage treatment sludge
- Industrial wastewater treatment sludge
- Pigsty manure sludge
- Food processing wastewater treatment sludge
- Septic tank sludge
Sewage Treatment Sludge
Sewage treatment sludge is generated at urban or regional sewage treatment facilities. These primarily come from domestic wastewater, stormwater, and industrial wastewater, and have high organic content and nutrient value. The components contained in the sludge are often utilized as renewable resources.
Industrial Wastewater Treatment Sludge
Industrial wastewater treatment sludge contains solids discharged from factories and industrial facilities. This sludge can contain heavy metals and various chemicals, raising concerns about environmental impact. Therefore, proper treatment based on legal regulations is required.
Pigsty Manure Sludge
Pigsty manure sludge is generated in the livestock industry, produced from the processing of pig manure. It mainly contains high levels of organic matter and is often reused as fertilizer, but proper treatment is necessary due to odor and potential pathogens.
Food Processing Wastewater Treatment Sludge
Food processing sludge is generated from food processing facilities and contains a high level of biodegradable organic matter. This type of sludge is generally used as organic fertilizer, but it requires strict hygiene management.
Septic Tank Sludge
Septic tank sludge is generated from septic tanks used in households and small-scale facilities. This sludge contains a lot of bacteria and organic matter, and if not properly treated, it can cause environmental pollution.
Sources and Characteristics
| Sources | Characteristics |
| Sewage Treatment Plants | High organic content and nutritional value |
| Industrial Wastewater Treatment Plants | Often contain heavy metals and chemicals |
| Agricultural Water Treatment Plants | Contain components that can be reused as soil or fertilizer |
| Household Septic Tanks | Contain a lot of bacteria and organic matter |
| Food Processing Facilities | Contain a high level of biodegradable organic matter |
The Importance of Sludge Treatment
Sludge has a significant impact on the environment. If sludge is not treated, it can cause water pollution, soil contamination, and odor problems. Additionally, sludge contains microorganisms and chemicals that pose risks to both the natural environment and human health.
Specific Impact Examples
- The decomposition of organic matter consumes a lot of oxygen, which can damage the ecosystems of rivers and lakes.
- Heavy metals can seep into groundwater, posing safety issues for drinking water.
Legal Regulations and Standards
Sludge treatment is strictly regulated by law, and appropriate treatment that meets these standards is required. Below are the main legal regulations and standards applied in Japan.
| Laws | Overview |
| Waste Management and Public Cleansing Law | This law pertains to the treatment and cleaning of waste, including industrial waste such as sludge. Non-compliance with appropriate treatment methods may result in penalties. |
| Water Pollution Control Law | This law sets standards for wastewater discharge from sludge treatment facilities, and compliance with these discharge standards are mandatory. |
| Hazardous Substances Regulations | Sludge containing specific hazardous substances must be treated in accordance with hazardous substances regulations, requiring special treatment methods. |
Adhering to these legal regulations and standards minimizes the negative environmental impact and ensures safe and effective sludge treatment.
Sludge Treatment Methods
The treatment method for sludge varies depending on its nature and contents. Generally, sludge is reduced in volume through processes like dewatering and incineration before its final disposal. Some types of sludge are recycled into compost or other materials. Here are some commonly known sludge treatment methods.
Incineration
This method involves burning sludge at high temperatures. It mainly reduces the volume of organic matter through combustion, removing odors and microorganisms. The heat generated from the incineration process can be used for generating electricity and heating. However, high-temperature incineration is costly and raises concerns about carbon dioxide emissions.
Types of Incineration
- Fluidized Bed Incineration
- Rotary Kiln Incineration
Landfill
This method involves stabilizing sludge and burying it in appropriate locations. Due to the presence of salts and heavy metals, pre-treatment and proper management are required. Limited landfill space makes this a less favorable long-term option.
Thickening/Dewatering
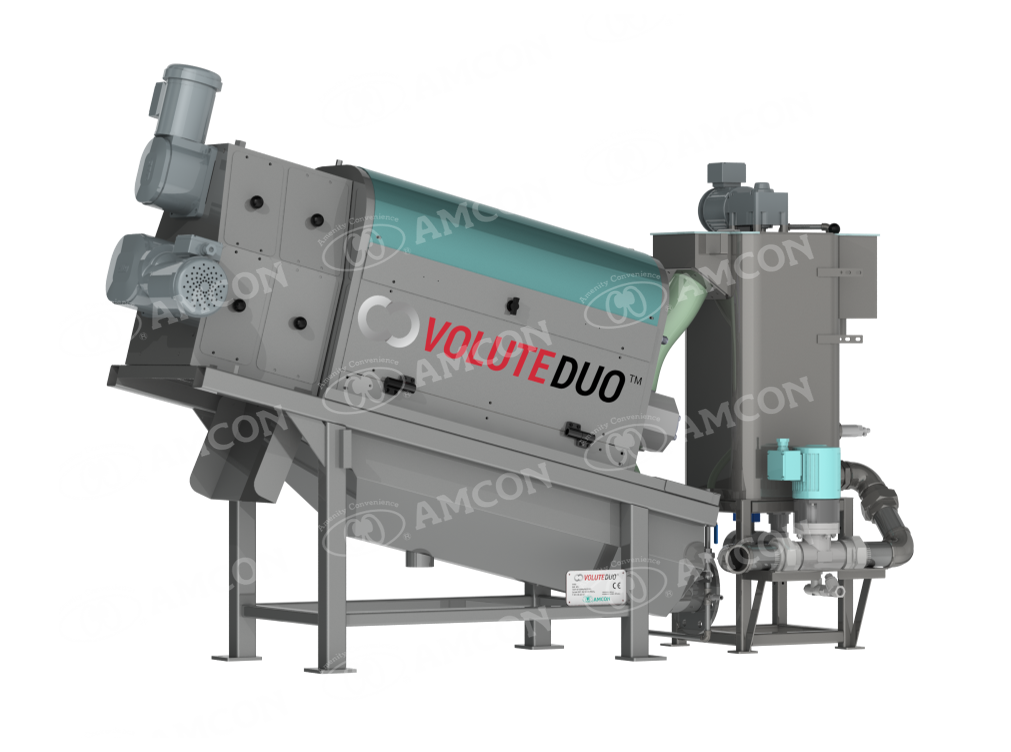
Since sludge contains a large amount of water, direct incineration or landfill disposal will be costly. Thickening and dewatering reduces the volume of sludge, thereby cutting down on disposal costs and environmental impacts. Dewatering also makes the sludge easier to handle and transport by converting it into a cake-like form. Thickened sludge remains in a liquid form, which can be beneficial for certain handling processes. The water separated during thickening and dewatering is treated and returned to the natural cycle.
For more details on sludge treatment using Sludge Dewatering Press/Sludge Thickener, click here ⇒
For more details on AMCON’s Sludge Dewatering Press/Sludge thickener, click here ⇒
Raw Materialization for Cement
This method involves drying and calcining sludge for reuse as a raw material in cement production. It neutralizes harmful substances in the sludge, allowing them to be used as resources. However, the sludge must meet certain standards to be suitable for this treatment.
Composting
Sludge containing organic matter is decomposed by microorganisms to create compost, which is reused as fertilizer in agriculture. Composting requires time and large spaces for processing large volumes of sludge.
Composting Process
- Pre-treatment
- Fermentation
- Maturation
Methane Fermentation
This method involves anaerobic microorganisms decomposing the organic matter in sludge to generate methane gas, which can be used as an energy source. Methane fermentation reduces sludge volume and enables energy recovery but requires specialized equipment and management.
Benefits of Methane Fermentation
- Energy recovery
- Reduction of organic matter
Granulation/Solidification
This method makes sludge easier to handle by converting it into solid form. The granulated sludge is easier to transport and can be reused or disposed of conveniently. It is often used in road construction and other building materials.
Melting
This high-temperature process melts sludge and converts inorganic substances into slag, which can be used as building materials. However, melting consumes high energy and has high initial equipment costs.
Products from Melting
- Slag
- Metal recovery
Oil-Water Separation
This method separates oil and water from sludge. The recovered oil can be recycled and reused as fuel, while the water is further treated and discharged or repurposed. Oil-water separation requires advanced technology but allows for effective resource utilization.
| Treatment Methods | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Incineration | Volume reduction, odor removal | High cost, CO2 emissions |
| Landfill | Simple | Requires management, environmental impact |
| Thickening/Dewatering | Volume reduction, easy handling | – |
| Raw Materialization for Cement | Effective resource utilization | Must meet standards |
| Composting | Usable in agriculture | Time-consuming, requires space |
| Methane Fermentation | Energy recovery | Requires management, equipment costs |
| Granulation/Solidification | Easy handling | Equipment cost |
| Melting | Usable as building materials | High energy consumption |
| Oil-Water Separation | Resource recycling | Requires advanced technology |
Introduction of New Sludge Treatment Technologies
Membrane Separation Technology
| Technology Name | Features | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Ultrafiltration | Uses fine membranes to separate solids | Efficient solid removal, reusable water quality | High cost, membranes prone to clogging |
| Nanofiltration | Uses even finer membranes to separate dissolved substances | High removal rate, can remove harmful substances | Very high cost, requires specialized management |
Membrane separation technology is used in both small- and medium-sized treatment plants as well as large-scale infrastructure facilities. For example, it has been implemented in urban sewage treatment facilities and industrial wastewater treatment plants. These technologies are particularly valuable in sites requiring efficient and high-quality water treatment.
High-Temperature and High-Pressure Treatment
Hydrothermal treatment, with its strong decomposition capabilities, can be applied to various organic sludges, such as food waste and agricultural waste. A practical example is the treatment of food sludge at a mayonnaise factory, where the treated sludge is used to generate biogas for energy.
Carbonization Treatment
In carbonization treatment, sludge is subjected to high temperatures in a carbonization furnace, converting it into carbon-rich material. These carbonized materials are often reused as soil conditioners or construction materials. For example, in Tokyo, carbonized materials are used in road construction projects.
Fertilization
Fertilization involves reusing sewage sludge as agricultural fertilizer. This method is commonly used by farmers, supporting sustainable agriculture. In agricultural regions like Hokkaido, this technology is widespread, with thousands of tons of sewage sludge being reused as fertilizer annually.
Amcom’s Sludge Dewatering and Fermentation System “Dell Compo”
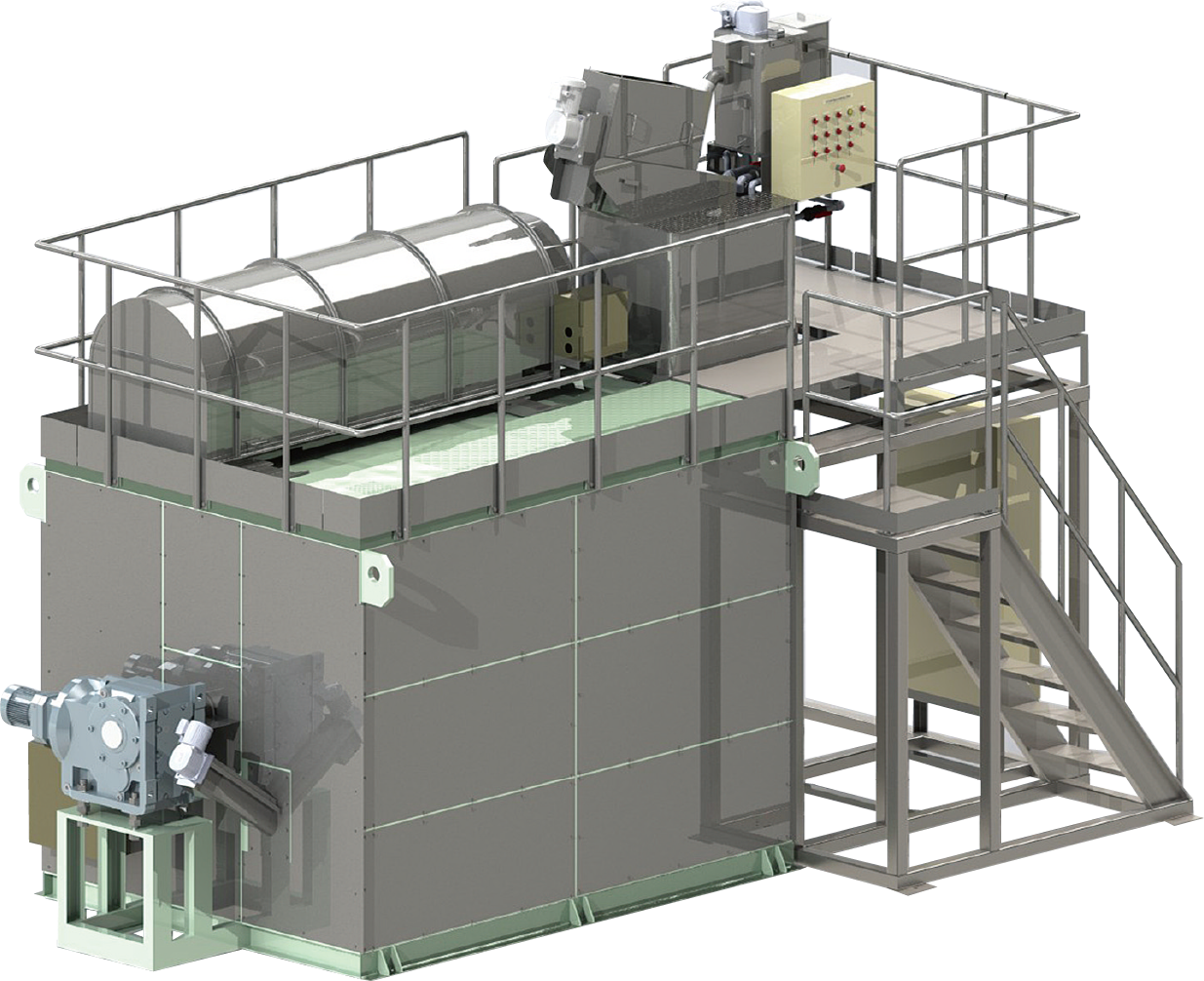
“Dell Compo” is a system designed for community wastewater treatment facilities serving 1,000 to 3,000 people. It integrates necessary equipment such as sludge dewatering machines, dryers, and fermentation tanks into a single unit, making it ideal for facilities with limited space. By converting sludge into fertilizer instead of choosing the costly option of disposal as industrial waste, it achieves zero sludge disposal costs and contributes to local sludge recycling.
*Note: Using fermented sludge as fertilizer requires registration with local authorities.
For more details on the Dell Compo sludge dewatering and fermentation system, click here ⇒
Energy Recovery
Energy recovery is often used to generate biogas or biodiesel. For instance, a sewage treatment plant in Yokohama City has implemented a system that generates biogas and uses it for power generation. This system produces millions of kWh of electricity annually, thus significantly reducing CO2 emissions.
Conclusion
This article introduced the methods and types of sludge treatment. The methods vary widely, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. From traditional methods like thickening, dewatering, incineration, and landfilling to newer technologies like methane fermentation and membrane separation, you can see here that there are numerous options to choose from. Selecting the appropriate method is crucial for reducing environmental impact. We hope this article has provided you with a better understanding of sludge treatment and its variants. If you have any questions or need further consultation on sludge treatment, please contact us.